|
Other Features |
|
Timeline & History TV Station Links Transmission Information Classic TV Guides Episode Guides |
|
TV Specials Guide TV3's 7pm Time-slot Tribute to Angela D'Audney New Zealand Information |
|
New
Zealand Information
|
|
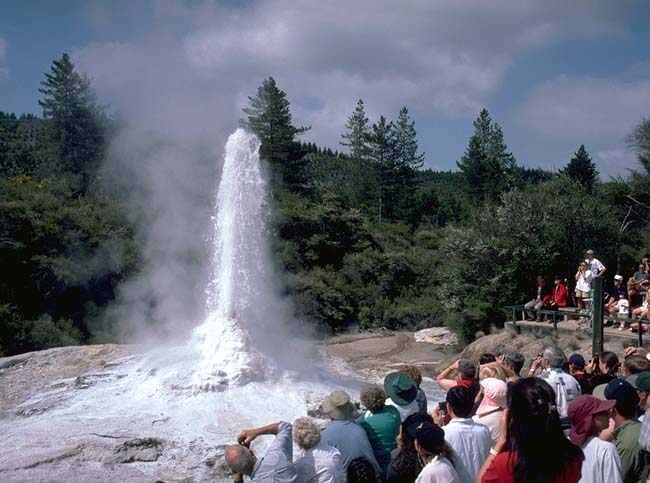
Aotearoa: Land of the Long White Cloud
|
| Main
New Zealand Facts:
location:
In the Southern
Hemisphere and is approximately 2250km east of Australia. It spans 1600
km from north to south, and is made up of the North Island, the South
Island, Stewart Island and various small surrounding islands.
population: Exactly 4 million people on New Zealand on 24 April 2003. Here is the latest population figure from Satistics NZ. language: The official languages are English and Mäori, and with New Zealand having the biggest polynesian population in the world there are many pacific Island languages spoken. the flag: It consists of two main elements, the Union flag of Great Britain and the four stars of the Southern Cross.
national anthem: It is called 'God Defend New Zealand", Here is the NZSO-played audio file and 'sheet music' of the national anthem. national sport: Rugby Union (Winter), Cricket (Summer) kiwiana stamp collection: icons and symbols of New Zealand are called kiwiana, here is one such collection from 1994 featured on stamps
links about new zealand: profile of NZ from a tourist point of view profile of NZ from a statistical point of view history of new zealand: visit the new zealand in history website general infomation: general information at the Kiwi Web website
the map of new zealand: 
Main
New Zealand Timeline: c1300 Polynesian settlement
established according to archaeological evidence. 1642 Dutch explorer Abel Tasman
discovers part of the coast of what was later named Nieuw Zeeland. 1769 Captain James Cook makes first
visit to New Zealand, charting the coast and claiming it in the name of
King George III. 1790’s- onwards, sealing, whaling,
timber and flax trades begin, sheep, cattle, horses poultry and new
plants introduced. 1833 James Busby arrives in Bay of
Islands after his appointment as British Resident in New Zealand. 1835 Declaration of Independence by
the United Tribes of New Zealand signed by some 34 Northern chiefs. 1840 Treaty of Waitangi signed between
the vast majority (nearly 500) of Maori Chiefs and Governor Hobson on
behalf of Queen Victoria. British sovereignty proclaimed. 1852 NZ Constitution Act passed
setting up a General Assembly and the first six provinces with a form of
representative government. 1859 Gold rushes start in Buller. 1860 Land wars start with Maori in
Taranaki and main conflicts end in Waikato in 1864 with extensive
confiscation's of tribal lands. 1867 Four Maori seats created in
Parliament and all Maori men over 21 get the vote, possibly the first
extension of the franchise without a property barrier in the world
(Pakeha (white) men got the vote in 1879). 1870 Last Imperial forces leave New
Zealand, Vogel Government starts major public works, railways and
immigration programmes which lead to arguments with some provinces. 1876 The provinces are abolished by
vote in the legislature. 1877 Education Act establishes a
national system of education to be free, secular and compulsory. 1886 Mount Tarawera erupts, killing
153 people and destroying world renowned pink and white terraces. 1893 All women were allowed to vote. 1894 Compulsory arbitration of
industrial disputes and reform of employment laws. 1898 Old Age Pension Act passed. 1908 Father of the atom, Ernest
Rutherford, is awarded the Nobel prize in Chemistry and New Zealand’s
population reaches one million. 1909 Stamp vending machine invented
and manufactured in New Zealand. 1914-18 Heavy losses in the First
World War (Passchendaele 3,700 New Zealanders killed). Six p.m. closing
introduced to pubs and draught beer alcohol content reduced. The
influenza epidemic killed an estimated 8,500 in New Zealand. 1915 New Zealand forces take part in
Gallipoli campaign. 1919 Returning soldiers just tip the
vote against prohibition. Prime Minister Massey signs the Treaty of
Versailles rather than the British on behalf of New Zealand 1929 Depression deepens and 1930
Unemployment Board set up for relief work. 1935 First Labour Government elected
in New Zealand. State housing programme launched. Working week reduced
to 40 hours. 1938 Social Security Act establishes
revised old age pensions and a national health service. 1939 Second World War, results in New
Zealanders participating in nearly every theatre of the war suffering
possibly the highest casualty rates per capita of any participant. 1945 New Zealand founder member of the
United Nations. 1946 Universal Family Benefit of one
pound a week. 1947 New Zealand Parliament adopts the
Statute of Westminster recognising New Zealand as a fully independent
state, although owing allegiance to the British King. 1948 Protest campaign against the
exclusion of Maori rugby players from rugby tour of South Africa (Maori
later declared honorary whites but protests got worse). 1950 Upper House of Parliament
abolishes itself (Government appoints enough new members who were known
as the "suicide squad"). New Zealand naval and ground forces
go to Korea. Boom in wool prices. 1951 Protracted 151 day waterfront
dispute destroys many strong nation-wide unions. 1952 Population reaches two million. 1953 First tour by a reigning monarch.
Edmund Hillary and sherpa Tenzing Norgay first to climb Mount Everest.
151 die in train wreck caused by volcanic lahar from Mt Ruapehu. 1960 Regular television programmes
(black and white) begin in Auckland 1961 Capital punishment abolished. 1965 New Zealand/Australia Free Trade
Agreement (NAFTA) signed. New Zealand sends troops to Vietnam and
protests begin. 1967 Referendum allows hotels to open
to 10/11 p.m. 1968 Roll-on roll-off ferry Wahine
sinks in harbour entrance storm, 51 die. 1969 Vote for 20 year olds. 1973 UK joins the EEC, New Zealand has
to negotiate entrance for butter/cheese/meat. Population reaches three
million. 1975 Waitangi Tribunal established to
start long process of resolving Maori claims for lost lands and taonga
(treasures). 1979 Air New Zealand plane crashes on
Antarctic Mt Erebus, 257 die. 1981 South African rugby tour brings
widespread social disruption and violence. 1982 loser Economic Relationship (CER)
signed with Australia, described internationally as one of the
"cleanest" free trade agreements in the world. One year long
wage and price and rent freeze imposed, but lasts until 1984. 1984 Labour Party under David Lange
wins snap election and Finance Minister Roger Douglas starts
de-regulation and other major reforms to turn-round.the economy. 1985 Anti-nuclear policy leads to
refusal of an American warship visit. French secret service agents
charged with manslaughter after bombing of Greenpeace’s Rainbow
Warrior in Auckland harbour. 1986 Goods and Services Tax introduced
on nearly everything, simultaneously with substantial reductions and
simplification in income tax. 1987 Labour Government was re-elected.
New Zealand’s first heart transplant. New Zealand wins World Rugby
Cup. Share prices plummet 60 percent in four months. 1990 New Zealand celebrates its 150th
birthday. Privatisation of major government enterprises continues as
does world wide economic downturn. National government under Jim Bolger
elected. 1992 Treaty of Waitangi Fisheries
Commission set up to administer fisheries assets on behalf of Maori, one
third of the commercial fishing quota also transferred to Maori hands
through Sealord Agreement. 1991 Employment Contracts Act passed,
effectively ending compulsory unionism. Unemployment reaches 200,000 and
starts to drop. 1993 National Government re-elected. 1995 New Zealand wins America’s Cup.
The Queen in person assented to the Act offering an apology and major
compensation under the Waikato Raupatu Settlement (Tainui Agreement),
the first of the large Maori iwi settlements under the latest Waitangi
Treaty claims legislation. 1996 Heads of Agreement reached
between the Crown and the Ngai Tahu iwi concerning Treaty claims
affecting virtually the whole South Island. Coalition Government under
Prime Minister Jim Bolger and Deputy Prime Minister Winston Peters
elected under proportional representation system ("MMP").
Unemployment down to six percent, Government in surplus for third year. 1997 Jim Bolger resigns as Prime
Minister and is replaced by New Zealand's first woman Prime Minister,
Jenny Shipley. Nga Tahu iwi signs a $170 million land settlement with
the Crown. After New Zealand hosted peace talks, the Defence Force
supervise opposing Bougainville groups in Papua New Guinea reaching a
truce agreement. National population increased 7% since 1991 to 3.6
million. The Auckland Skytower is opened.
New
Zealand Events Timeline: c1300 Archaeological
evidence indicates that Polynesian settlement was established by this
date.
1642 Dutch
explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman discovers a land he calls Staten Landt,
later named Nieuw Zeeland.
1769 British
explorer James Cook makes the first of three visits to New Zealand,
taking possession of the country in the name of King George III.
1790s Sealing,
deep-sea whaling, the flax and timber trades begin, with some small
temporary settlements. First severe introduced epidemic among Mäori
population.
1791 First
visit by a whaling vessel, the "William and Ann", to Doubtless
Bay.
1806 First
Päkehä women arrive in New Zealand. 1814 British
missionary Samuel Marsden makes first visit to New Zealand. Anglican
mission station established. Sheep, cattle, horses and poultry are
introduced.
1815 Thomas
Holloway King is the first Päkehä child born in New Zealand.
1819 Raids
on Taranaki and Te Whanganui-a-tara regions by Ngapuhi and Ngäti Toa
people led by chiefs Patuone, Nene, Moetara, Tuwhare and Te Rauparaha.
1820 Hongi
Hika, Ngapuhi chief, visits England, meets King George IV and secures
supply of muskets.
1821 Musket
wars begin with raids by Hongi Hika and Te Morenga on southern iwi and
continue throughout the decade.
1822 Ngäti
Toa migration south to Cook Strait region, led by Te Rauparaha, begins.
1823 Jurisdiction
of New South Wales courts is extended to British citizens in New
Zealand. Wesleyan Missionary Society mission established. First Church
of England marriage between Philip Tapsell and Mäori girl, Maria Ringa.
1824 Te
Heke Niho-puta migration of Taranaki iwi to the Kapiti Coast. Rawiri
Taiwhanga in Bay of Islands sells dairy produce and other food supplies
to visiting ships.
1827 Te
Rauparaha's invasion of the South Island from Kapiti begins.
1830 First
acorn planted at Waimate North where agricultural mission and school
established.
1831 Whaling
stations established at Tory Channel and Preservation Inlet.
1833 James
Busby, appointed British Resident in New Zealand, arrives at the Bay of
Islands.
1834 United
Tribes' flag adopted by some 25 northern chiefs at Busby's suggestion.
1835 Declaration
of Independence by the "United Tribes of New Zealand" signed
by 34 northern chiefs.
1837 New
Zealand Association formed in London, becoming the New Zealand
Colonisation Society in 1838 and the New Zealand Company in 1839, under
the inspiration of Edward Gibbon Wakefield. William Colenso completes
printing the New Testament in Mäori, the first book printed in New
Zealand. 1838 Bishop
Pompallier founds Roman Catholic Mission at Hokianga.
1839 William
Hobson instructed to establish British rule in New Zealand, as a
dependency of New South Wales. Colonel William Wakefield of the New
Zealand Company arrives on the "Tory" to purchase land for a
settlement.
1840 New
Zealand Company settlers arrive at Port Nicholson, Wellington. Treaty of
Waitangi signed at Bay of Islands and later over most of the country.
British sovereignty proclaimed. French settlers land at Akaroa. Hobson
becomes first Governor and sets up executive and legislative councils.
1841 European
settlements established at New Plymouth and Wanganui. Capital shifted
from Kororareka to Auckland.
1842 Main
body of settlers arrive at Nelson. 1843 Twenty-two
European settlers and four Mäori killed at a confrontation at Tua
Marina, near the Wairau, in Marlborough. Robert FitzRoy becomes
Governor.
1844 Hone
Heke begins the "War in the North". New Zealand Company
suspends its colonising operations due to financial difficulties.
1845 George
Grey becomes Governor.
1846 War
in the north ends with capture of Ruapekapeka. First New Zealand
Constitution Act passed. Heaphy, Fox and Brunner begin exploring the
West Coast. First steam vessel, HMS "Driver", arrives in New
Zealand waters.
1848 Settlement
founded by Scottish Otago Association. Provinces of New Ulster and New
Munster set up under 1846 Act. Coal discovered at Brunner on the West
Coast. Earthquake in Marlborough damages most Wellington buildings. 1850 Canterbury
settlement founded. 1852 Second
New Zealand Constitution Act passed creating General Assembly and six
provinces with representative government. 1853 Idea
of a Mäori King canvassed by Tamihana Te Rauparaha and Matene Te
Whiwhi.
1854 First
session of the General Assembly opens in Auckland.
1855 Governor
Thomas Gore Browne, appointed in 1854, arrives. Severe earthquake on
both sides of Cook Strait. Adhesive, imperforate postage stamps on sale.
1856 Henry
Sewell forms first ministry under responsible government and becomes
first Premier. Edward Stafford forms first stable ministry.
1858 New
Provinces Act passed. Te Wherowhero installed as first Mäori King,
taking name Potatau I.
1859 First
session of Hawke's Bay and Marlborough provincial councils. Gold
discovered in Buller River. New Zealand Insurance Company established.
1860 Waitara
dispute develops into general warfare in Taranaki.
1861 Grey
begins second governorship. Gold discovered at Gabriel's Gully; Otago
goldrushes begin. First session of Southland provincial council. Bank of
New Zealand incorporated at Auckland. 1862 First
electric telegraph line opens—from Christchurch to Lyttleton. First
gold shipment from Dunedin to London. 1863 War
resumes in Taranaki and begins in Waikato when General Cameron crosses
the Mangatawhiri stream. New Zealand Settlements Act passed to effect
land confiscation. First steam railway in New Zealand opened.
1864 War
in the Waikato ends with battle of Orakau. Land in Waikato, Taranaki,
Bay of Plenty and Hawke's Bay confiscated. Gold discovered in
Marlborough and Westland. Arthur, George and Edward Dobson are the first
Päkehä to cross what becomes known as Arthur's Pass. 1865 Seat
of government transferred from Auckland to Wellington. Native Land Court
established. Mäori resistance continues. Auckland streets lit by gas
for first time.
1866 Cook
Strait submarine telegraph cable laid. Christchurch to Hokitika road
opens. Cobb and Co. coaches run from Canterbury to the West Coast.
1867 Thames
goldfield opens. Four Mäori seats established in Parliament. Lyttleton
railway tunnel completed. Armed constabulary established. 1868 Mäori
resistance continues through campaigns of Te Kooti Arikirangi and
Titokowaru. New Zealand's first sheep breed, the Corriedale, is
developed. 1869 New
Zealand's first university, the University of Otago, is established. 1870 The
last imperial forces leave New Zealand. Vogel's public works and
immigration policy begins. New Zealand University Act passed,
establishing a federal system which lasts until 1961. Vogel announces
national railway construction programme; over 1,000 miles constructed by
1879. First rugby match. Auckland to San Francisco mail service begins.
1871 Deer
freed in Otago.
1872 Te
Kooti retreats to the King Country and Mäori armed resistance ceases.
Telegraph communication links Auckland, Wellington and southern
provinces.
1873 New
Zealand Shipping Company established. 1874 First
New Zealand steam engine built at Invercargill. 1876 Abolition
of the provinces and establishment of local government by counties and
boroughs. New Zealand-Australia telegraph cable established.
1877 Education
Act passed, establishing national system of primary education.
1878 Completion
of Christchurch-Invercargill railway. 1879 Triennial
Parliaments Act passed. Vote is given to every male aged 21 and over.
Kaitangata mine explosion, 34 people die. Annual property tax
introduced.
1881 Parihaka
community forcibly broken up by troops. Te Whiti, Tohu Kakahi and
followers arrested and imprisoned. Wreck of SS "Tararua", 131
people die. Auckland and Christchurch telephone exchanges open.
1882 First
shipment of frozen meat leaves Port Chalmers for England on the
"Dunedin".
1883 Te
Kooti pardoned, Te Whiti and other prisoners released. Direct steamer
link established between New Zealand and Britain. 1884 King
Tawhiao visits England with petition to the Queen, appealing to the
Treaty of Waitangi, and is refused access. First overseas tour by a New
Zealand rugby team, to New South Wales. Construction of King Country
section of North Island main trunk railway begins. 1886 Mt
Tarawera erupts and the Pink and White Terraces are destroyed, 153
people die. Oil is discovered in Taranaki. 1887 New
Zealand's first national park, Tongariro, is presented to the nation by
Te Heuheu Tukino IV. Reefton becomes first town to have electricity.
First inland parcel post service.
1888 Birth
of writer Katherine Mansfield. 1889 Abolition
of non-residential or property qualification to vote. First New
Zealand-built locomotive completed at Addington. 1890 Maritime
Strike involves 8000 unionists. "Sweating" Commission reports
on employment conditions. First election on a one-man one-vote basis.
1891 John
McKenzie introduces the first of a series of measures to promote closer
land settlement. John Ballance becomes Premier of first Liberal
Government.
1892 First
Kotahitanga Mäori Parliament meets. 1893 Franchise
extended to women. John Ballance dies and is succeeded by Richard John
Seddon. Liquor licensing poll introduced. Elizabeth Yates becomes first
woman mayor, of Onehunga. Banknotes become legal tender. 1894 Compulsory
arbitration of industrial disputes and reform of employment laws.
Advances to Settlers Act. Clark, Fyfe and Graham become the first people
to climb Mt Cook. Wreck of SS "Wairarapa". 1896 National
Council of Women is founded. Brunner Mine explosion, 67 people killed.
Census measures national population as 743,214. 1897 First
of series of colonial and later imperial conferences held in London.
Apirana Ngata and others form Te Aute College Students' Association.
1898 Old
Age Pensions Act. First cars imported to New Zealand. 1899 New
Zealand army contingent is sent to the South African war. First
celebration of Labour Day.
1900 Mäori
Councils Act passed. Public Health Act passed setting up Department of
Public Health in 1901.
1901 Cook
and other Pacific Islands annexed. Penny postage first used.
1902 Pacific
cable begins operating between New Zealand, Australia and Fiji. Wreck of
SS "Elingamite".
1904 Richard
Pearse achieves semi-controlled flight near Timaru.
1905 New
Zealand rugby team tours England and becomes known as the All Blacks.
Old Age Pension increases to £26 per year; however, eligibility
tightened.
1906 Seddon
dies and is succeeded by Joseph Ward as Premier. 1907 New
Zealand constituted as a Dominion. Fire destroys Parliament buildings.
1908 Auckland
to Wellington main trunk railway line opens. Ernest Rutherford is
awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. New Zealand's population reaches
one million.
1909 "Red"
Federation of Labour formed. SS "Penguin" wrecked in Cook
Strait, 75 people die. Compulsory military training introduced.
Stamp-vending machine invented and manufactured in New Zealand. 1910 Halley's
Comet sighted in New Zealand. 1912 William
Massey wins vote in the House and becomes first Reform Party Prime
Minister. Waihi miners strike.
1913 Waterfront
strikes in Auckland and Wellington. 1914 World
War I begins and German Samoa is occupied. New Zealand Expeditionary
Forces are despatched to Egypt. Huntly coal mine disaster, 43 people
die.
1915 New
Zealand forces take part in Gallipoli campaign. Reform and Liberal
parties form National War Cabinet. Britain announces its intention to
purchase all New Zealand meat exports during war. 1916 New
Zealand troops transfer from Western Front. Conscription introduced.
Labour Party formed. Lake Coleridge electricity supply scheme opened.
1917 Battle
of Passchendaele, 3,700 New Zealanders killed. Six o'clock public house
closing introduced. Lord Liverpool becomes first Governor-General.
1918 New
Zealand Division in the Battle of the Somme. End of World War I.
Influenza epidemic in which an estimated 8,500 die. Creation of power
boards for electricity distribution. Prohibition petition with 242,001
signatures presented to Parliament.
1919 Women
eligible for election to Parliament. Massey signs Treaty of Versailles.
First official airmail flight from Auckland to Dargaville.
1920 Anzac
Day established. New Zealand gets League of Nations mandate to govern
Western Samoa. First aeroplane flight across Cook Strait. 1921
New Zealand Division of Royal Navy established. 1921
New Zealand Division of Royal Navy
established.
1922 Meat
Producers' Board placed in control of meat exports. 1923 Otira
tunnel opens. Ross Dependency proclaimed. Death of Katherine Mansfield.
1926 National
public broadcasting begins under auspices of Radio Broadcasting Co. Ltd.
1928 New
Zealand Summer Time introduced. General election won by new United
Party. Kingsford-Smith completes first flight across Tasman Sea.
1929 Economic
depression gets worse. Severe earthquake in Murchison-Karamea district,
17 people die. First health stamps issued. 1930 Unemployment
Board set up to provide relief work. 1931 Newly
formed Coalition Government under George Forbes wins general election.
Hawke's Bay earthquake, 256 die. Substantial percentage reductions in
public service wages and salaries. Airmail postage stamps introduced.
1932 Compulsory
arbitration of industrial disputes abolished. Unemployed riots in
Auckland, Dunedin and Christchurch. Reductions in old-age and other
pensions.
1933 Elizabeth
McCombs becomes first woman MP. Distinctive New Zealand coins first
issued.
1934 Reserve
Bank and Mortgage Corporation established. First trans-Tasman airmail.
1935 First
Labour Government elected under Michael Joseph Savage. Air services
begin across Cook Strait.
1936 Reserve
Bank taken over by state. State housing programme launched. Guaranteed
prices for dairy products introduced. National Party formed from former
Coalition MPs. Inter-island trunk air services introduced. Jack Lovelock
wins New Zealand's first Olympic gold. Jean Batten's record flight from
England. Working week reduced from 44 to 40 hours. 1937 Federation
of Labour unifies trade union movement. RNZAF set up as separate branch
of armed forces.
1938 Social
Security Act establishes revised pensions structure and the basis of a
national health service. Import and exchange controls are introduced.
1939 World
War II begins. Second New Zealand Expeditionary Force formed. Bulk
purchases of farm products by Great Britain. HMS "Achilles"
takes part in Battle of the River Plate.
1940 Michael
Joseph Savage dies and is succeeded by Peter Fraser. Sidney Holland
becomes Leader of Opposition. Conscription for military service. German
mines laid across Hauraki Gulf.
1941 Japan
enters the war. Mäori War Effort Organisation set up. Pharmaceutical
and general practitioner medical benefits introduced. 1942 Economic
stabilisation. New Zealand troops in Battle of El Alamein. Food
rationing introduced. Mobilisation of women for essential work.
1943 New
Zealand troops take part in invasion of Italy. 1944 Australia-New
Zealand Agreement provides for co-operation in the South Pacific.
1945 War
in Europe ends on 8 May and in the Pacific on 15 August. New Zealand
signs United Nations charter. Mäori Social and Economic Advancement Act
passed. National Airways Corporation founded. 1946 Family
benefit of £1 per week becomes universal. Bank of New Zealand
nationalised.
1947 Statute
of Westminster adopted by New Zealand Parliament. First public
performance by National Orchestra. Mabel Howard becomes first woman
cabinet minister. Fire in Ballantyne's department store, Christchurch,
41 people die.
1948 Protest
campaign against exclusion of Mäori players from rugby tour of South
Africa. Polio epidemic closes schools. Ruapehu and Ngauruhoe erupt. Meat
rationing ends.
1949 Referendum
agrees to compulsory military training. National Government elected. New
Zealand gets first four navy frigates. 1950 Naval
and ground forces sent to Korean War. Legislative Council abolished.
Wool boom.
1951 Prolonged
waterfront dispute—state of emergency proclaimed. ANZUS treaty signed
between United States, Australia and New Zealand. Mäori Women's Welfare
League established. 1952 Population
reaches over two million. 1953 First
tour by a reigning monarch. Edmund Hillary and Sherpa Tenzing Norgay
first to climb Mount Everest. Railway disaster at Tangiwai, 151 people
die. World sheep-shearing record set by Godfrey Bowen. 1954 New
Zealand signs South East Asia Collective Defence Treaty. Gains seat on
United Nations Security Council. Social Credit gets 10 percent of vote
in general election, but no seat in Parliament. 1955 Pulp
and paper mill opens at Kawerau. Rimutaka rail tunnel opened.
1956 New
Zealand troops sent to Malaya. Roxburgh and Whakamaru power stations in
operation.
1957 National
loses election; Walter Nash leads second Labour Government. Last
hanging. Scott Base established in Ross Dependency. Court of Appeal
constituted. Dairy products gain 10 years of unrestricted access to
Britain.
1958 PAYE
tax introduced. Arnold Nordmeyer's "Black Budget". First
geothermal electricity generated at Wairakei. First heart-lung machine
used at Greenlane Hospital, Auckland.
1959 Antarctic
Treaty signed with other countries involved in scientific exploration in
Antarctica. Auckland harbour bridge opened. 1960 Regular
television programmes begin in Auckland. National Government elected.
Government Service Equal Pay Act passed. 1961 New
Zealand joins the International Monetary Fund. Capital punishment
abolished.
1962 New
Zealand troops sent to Malaysia during "confrontation" with
Indonesia. Western Samoa becomes independent. Sir Guy Powles becomes
first Ombudsman. New Zealand Mäori Council established. Cook Strait
rail ferry service begins. Taranaki gas well opens. Peter Snell
establishes mile and half-mile world running records. 1964 Marsden
Point oil refinery opens at Whangarei. Cook Strait power cables laid.
Auckland's population reaches half a million. 1965 NAFTA
agreement negotiated with Australia. Support for United States in
Vietnam; New Zealand combat force sent, protest movement begins. Cook
Islands becomes self-governing.
1966 International
airport officially opens at Auckland. New Zealand labour force reaches
one million. National Library of New Zealand created. Te
Ata-i-rangi-kaahu becomes first Mäori Queen.
1967 Referendum
extends hotel closing hours to 10pm. Decimal currency introduced. Lord
Arthur Porritt becomes first New Zealand-born Governor-General. Breath
and blood tests introduced for suspected drinking drivers. 1968
Inter-island ferry "Wahine" sinks in severe storm in
Wellington Harbour, 51 people die. Three die in Inangahua earthquake. 1968 Inter-island
ferry "Wahine" sinks in severe storm in Wellington Harbour, 51
people die. Three die in Inangahua earthquake. 1969 Vote
extended to 20-year-olds. National Government wins fourth election in a
row. First output from Glenbrook Steel Mill. 1970 Natural
gas from Kapuni supplied to Auckland. 1971 New
Zealand secures continued access of butter and cheese to the United
Kingdom. Nga Tamatoa protest at Waitangi celebrations. Tiwai Point
aluminium smelter begins operating. Warkworth satellite station begins
operation.
1972 Labour
Government led by Norman Kirk elected. Equal Pay Act passed.
1973 Great
Britain becomes a member of the EEC. Naval frigate despatched in protest
against French nuclear testing in the Pacific. New Zealand's population
reaches three million. Rugby tour of South Africa cancelled. Oil price
hike means worst terms of trade in 30 years. Colour TV introduced. 1974 Prime
Minister Norman Kirk dies. Commonwealth Games held in Christchurch.
1975 Robert
Muldoon becomes Prime Minister after National election victory. Mäori
land march protests against land loss. The Waitangi Tribunal is
established. Second TV channel starts broadcasting. 1976 Matrimonial
Property Act passed. Pacific Islands "overstayers" deported.
EEC import quotas for New Zealand butter set until 1980. Introduction of
metric system of weights and measures. Subscriber toll dialling
introduced.
1977 National
Superannuation scheme begins. New Zealand signs the Gleneagles
Agreement. The 200-mile exclusive economic zone is established. Bastion
Point occupied by protesters.
1978 Registered
unemployed reaches 25,000. National Government re-elected.
1979 Air
New Zealand plane crashes on Mount Erebus, Antarctica, 257 people die.
Carless days introduced to reduce petrol consumption. 1980 Social
Credit wins East Coast Bays by-election. Saturday trading partially
legalised. Eighty-day strike at Kinleith Mill. 1981 South
African rugby team's tour brings widespread disruption. 1982 CER
agreement signed with Australia. First köhanga reo established.
Year-long wage, price and rent freeze imposed—lasts until 1984. 1983 Visit
by nuclear-powered United States Navy frigate "Texas" sparks
protests. Official Information Act replaces Official Secrecy Act. New
Zealand Party founded.
1984 Labour
Party wins snap general election. Finance Minister Roger Douglas begins
deregulating the economy. New Zealand ratifies the United Nations
Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against
Women. Te Hikoi ki Waitangi march and disruption of Waitangi Day
celebrations. Auckland's population exceeds that of the South Island.
Government devalues New Zealand dollar by 20 percent.
1985 Anti-nuclear
policy leads to refusal of a visit by the American warship, the USS
"Buchanan". Greenpeace vessel Rainbow Warrior bombed and sunk
by French agents in Auckland harbour. New Zealand dollar floated. Keri
Hulme wins Booker Prize for "The Bone People". First case of
locally-contracted AIDS is reported. Waitangi Tribunal given power to
hear grievances arising since 1840.
1986 Homosexual
Law Reform Bill passed. Royal Commission reports in favour of MMP
electoral system. Jim Bolger becomes National Party leader. Soviet
cruise ship, the "Mikhail Lermontov", sinks in Marlborough
Sounds. Goods and Services Tax introduced. First visit to New Zealand by
the Pope.
1987 Share
prices plummet by 59 percent in four months. Labour wins general
election. Mäori Language Act making Mäori an official language passed.
Anti-nuclear legislation enacted. First lotto draw. New Zealand's first
heart transplant is performed. New Zealand wins Rugby World Cup.
Significant earthquake in the Bay of Plenty.
1988 Number
of unemployed exceeds 100,000. Bastion Point land returned to Mäori
ownership. Combined Council of Trade Unions formed. Royal Commission on
Social Policy issues April Report. Gibbs Report on hospital services and
Picot Report on education published. State Sector Act passed. Cyclone
Bola strikes northern North Island. Electrification of North Island's
main trunk line completed. New Zealand Post closes 432 post offices.
Fisheries quota package announced for Mäori iwi.
1989 Prime
Minister David Lange suggests formal withdrawal from ANZUS. Jim Anderton
founds NewLabour Party. Lange resigns and Geoffrey Palmer becomes Prime
Minister. First annual balance of payments surplus since 1973. Reserve
Bank Act sets bank's role as one of maintaining price stability. First
school board elections under Tomorrow's Schools reforms. First elections
under revised local government structure. Sunday trading begins. Third
TV channel begins. 1990 New
Zealand celebrates its sesquicentennial. Mäori leaders inaugurate
National Congress of Tribes. Dame Catherine Tizard becomes first woman
Governor-General. Geoffrey Palmer resigns as Prime Minister and is
replaced by Mike Moore. National Party has landslide victory. Jim Bolger
becomes Prime Minister. One and two cent coins are no longer legal
tender. Commonwealth Games are held in Auckland. Telecom sold for $4.25
billion. Welfare payments cut. Big earthquake in Hawke's Bay. 1991 First
budget of new Finance Minister, Ruth Richardson. Welfare payments
further reduced. The Alliance Party is formed. Employment Contracts Act
passed. Consumers Price Index has lowest quarterly increase for 25
years. Number of unemployed exceeds 200,000 for the first time. New
Zealand troops join multi-national force in the Gulf War. An avalanche
on Mt Cook reduces its height by 10.5 metres.
1992 Government
and Mäori interests negotiate Sealords fisheries deal. Public health
system reforms. State housing commercialised. Watties Foods is bought by
American company, Heinz. New Zealand gets seat on United Nations
Security Council. 1993 Centennial
of women's suffrage celebrated. New Zealand First Party launched by
Winston Peters. National wins election without majority—Opposition MP
Peter Tapsell becomes Speaker of the House, thus giving the government a
majority. Referendum favours MMP electoral system. New Zealand film
"The Piano" has international success. 1994 Government
commits 250 soldiers to front-line duty in Bosnia. Government proposes
$1 billion cap in plan for final settlement of Treaty of Waitangi
claims. Sharemarket reaches highest level since 1987 crash. New
Zealand's first casino opens in Christchurch. First fast-ferry passenger
service begins operation across Cook Strait.
1995 Team
New Zealand wins America's Cup. Occupation of Moutua Gardens, Wanganui.
Waikato Raupatu Claims Settlement Act passed. New political parties
form: the Conservative, Christian Heritage and United New Zealand.
Renewal of French nuclear tests results in New Zealand protest flotilla
and navy ship "Tui" sailing for Moruroa Atoll. Commonwealth
Heads of Government Meeting in Auckland, Nelson Mandela visits. New
Zealand contingent returns from Bosnia.
1996 Imported
pests—Mediterranean fruit flies and white-spotted tussock
moths—cause disruption to export trade and to Aucklanders. Thirteenth
National Park, Kahurangi, opened in north-west Nelson. Waitangi Tribunal
recommends generous settlement of Taranaki land claims. First legal
sports betting at TAB. $170 million Ngai Tahu settlement proposed, $40
million Whakatohea settlement announced. First MMP election brings
National/New Zealand First coalition government. 1997 America's
Cup damaged in attack by a Mäori activist. TV4 begins daily broadcasts.
Customs Service cracks down on imported Japanese used cars following
claims of odometer fraud. Auckland's Skytower is opened. Beatrice
Faumuina wins gold for discus at the World Track and Field championships
in Athens. Auckland band OMC's album "How Bizarre" goes gold
in the United States. Compulsory superannuation is rejected by a margin
of more than 9 to 1 in New Zealand's first postal referendum. Jim Bolger
resigns as Prime Minister after a National Party coup; he is replaced by
New Zealand's first woman Prime Minister, Jenny Shipley.
1998 Auckland city businesses hit by a power cut lasting several weeks. The crisis continues for over a month and results in an inquiry into Mercury Energy. The women's rugby team, the Black Ferns, become the world champions. Mortgage rates and the New Zealand dollar both take a slide leaving NZ$1 below the US50c mark for the first time in 12 years. The Coalition Government is dissolved leaving the Jenny Shipley-led National party as a minority government. Several cases of tuberculosis discovered in South Auckland in the worst outbreak for a decade. The Hikoi of Hope marches to Parliament calling for more support for the poor. The government announces plans to lease 28 new fighter aircraft but says no to a new naval frigate.
|